Introduction to the Observatory
Visibility Observations

Visibility is the maximum distance at which an object can be seen with the naked eye.
Since 1963, the Seikei Meteorological Observatory has continuously monitored the number of days when Mount Fuji, located approximately 83 km southwest, and Tokyo Tower, located approximately 17 km east-southeast, are visible from the school rooftop. This observation has also been conducted for the Chichibu Mountain Range, high-rise buildings in Shinjuku, the chimney of the Suginami Incineration Plant in Takaido, Mount Tsukuba, and Tokyo Skytree.
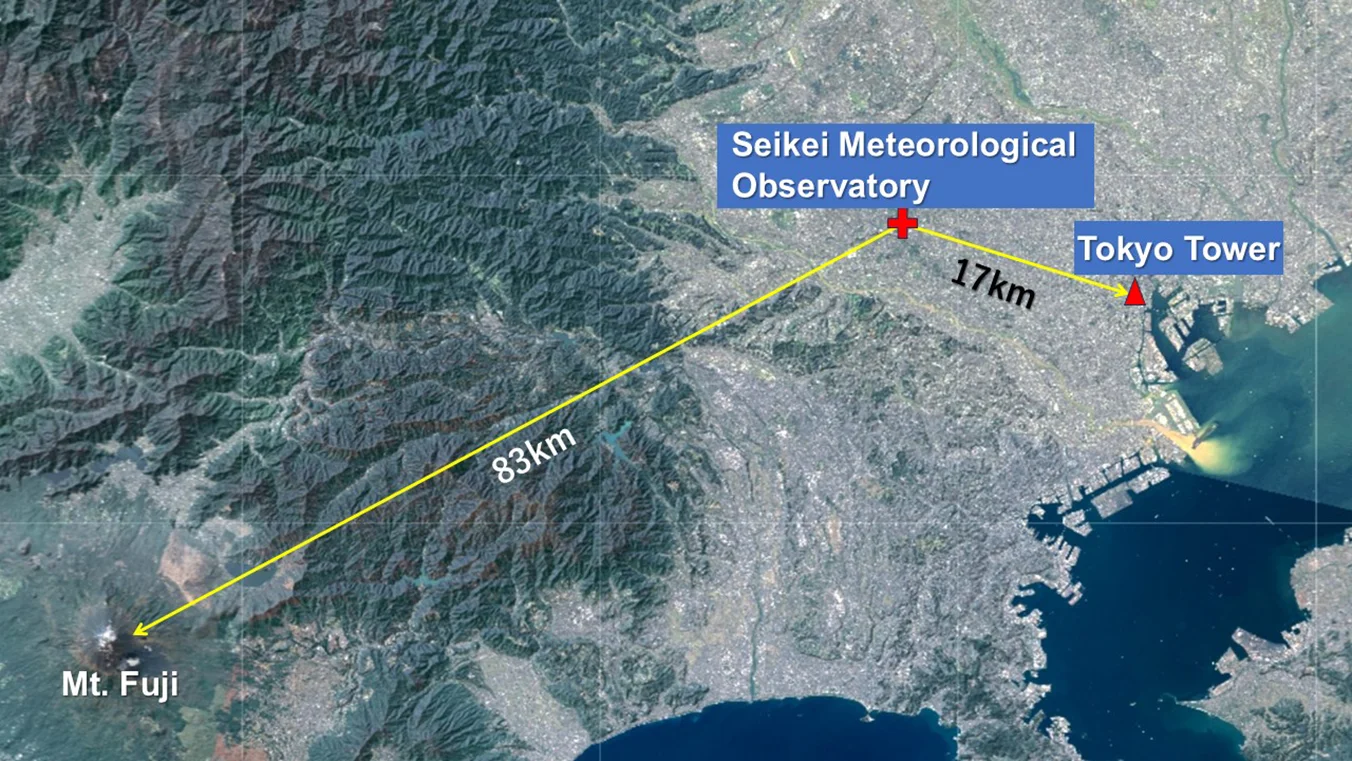
Created by modifying a Geographical Survey Institute map (Geospatial Information Authority of Japan)
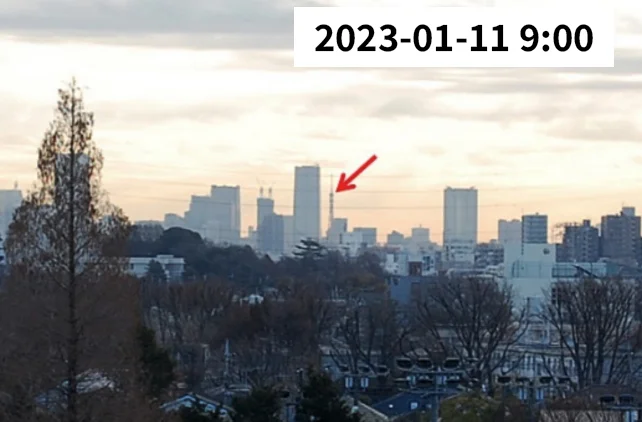
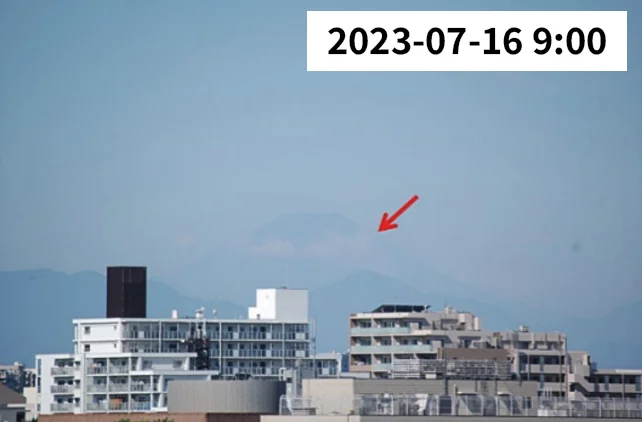
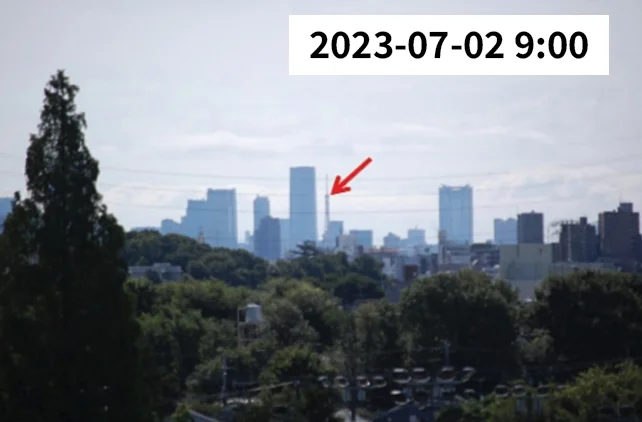




Mount Fuji (left) and Tokyo Tower (right) as seen from the school building rooftop
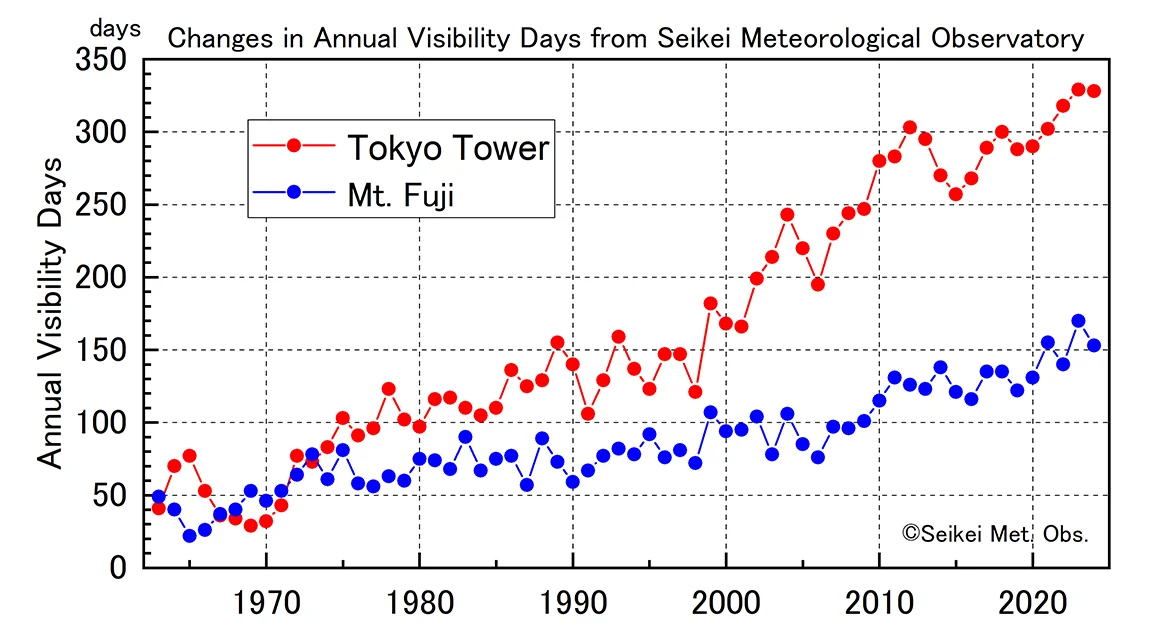
The following graph shows the annual variation in visibility days for Mount Fuji and Tokyo Tower over the past approximately 60 years. In the 1960s, visibility days for both were around 50 days per year. In recent years, however, the number of days Mount Fuji is visible has increased significantly, exceeding 150 days per year. Visibility days for Tokyo Tower in the direction of central Tokyo have also increased approximately sixfold to around 300 days. This is thought to be due to improvements of air pollution in the central Tokyo area.